The researchers chemically modified liquid latexes to make them printable and built a custom 3-D printer with an embedded computer vision system to print accurate, high-resolution features of this high-performance material.Scott ran into a fundamental challenge: liquid latex is extremely fragile and difficult for chemists to alter. "Latexes are in a state of Zen," "If you add anything to it, it'll completely lose its stability and crash out."
Then, the chemists came up with a new idea: What if Scott built a scaffold, similar to those used in building construction, around the latex particles to hold them in place? This way, the latex could maintain its great structure, and Scott could add photoinitiators and other compounds to the latex to enable 3-D printing with ultraviolet (UV) light.
"When designing the scaffold, the biggest thing you have to worry about is stability of everything," Scott said. "It took a lot of reading, even stuff as basic as learning why colloids are stable and how colloidal stability works, but it was a really fun challenge."
The researchers chose to use a process called vat photopolymerization, in which the printer uses UV light to cure, or harden, a viscous resin into a specific shape.
Even with the custom printer, the fluid latex particles caused scattering outside of the projected UV light on the latex resin surface, which resulted in printing inaccurate parts, so Meenakshisundaram devised a second novel idea. He embedded a camera onto the printer to capture an image of each vat of latex resin. With his custom algorithm, the machine is able to "see" the UV light's interaction on the resin surface and then automatically adjust the printing parameters to correct for the resin scattering to cure just the intended shape.
"An interpenetrating polymer network is like catching fish in a net," Meenakshisundaram said. "The scaffold gives it a shape. Once you put that in the oven, the water will evaporate, and the tightly coiled polymer chains can relax, spread or flow, and interpenetrate into the net."
photopolymer?
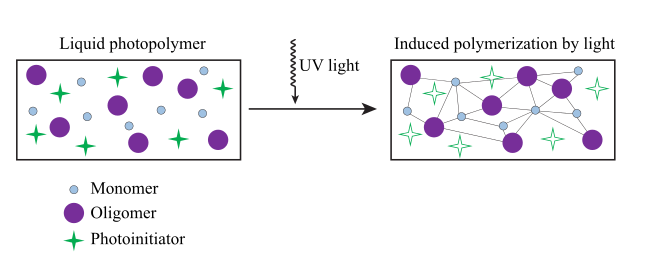
A photopolymer or light-activated resin is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light
One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers.[
기존의 Vat photopolymerization

그러나 기존의 방법의 경우, high molecular weight polymers are not amenable to VP due to concomitant high solution and melt viscosities. Thus, a challenging paradox arises between printability and mechanical performance.
Vat polymerization를 개발한 분.
논문에서 사용된 것.

reference
Philip J. Scott et al. 3D Printing Latex: A Route to Complex Geometries of High Molecular Weight Polymers, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2020). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b19986
'3D print' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 3d printed aorta & heart valve (0) | 2020.08.30 |
|---|---|
| 3d printing embryoid body (0) | 2020.08.12 |
| Non-invasive 3D printing in living creature (0) | 2020.06.29 |
| 3D 프린터로 움직이는 세포 위에 센서 만들기. (0) | 2020.06.18 |
| 4D 프린팅 (0) | 2020.06.15 |



