Separation and characterization of cancer cells are essential for early diagnosis of peritoneal metastasis. However, due to the low content of cancer cells in patients' peritoneal lavages, traditional detection methods lack sensitivity and cannot satisfy clinical demand.
jointly proposed an optically induced electrokinetics (OEK) microfluidic method for label-free separation and characterization of gastric cancer cells.
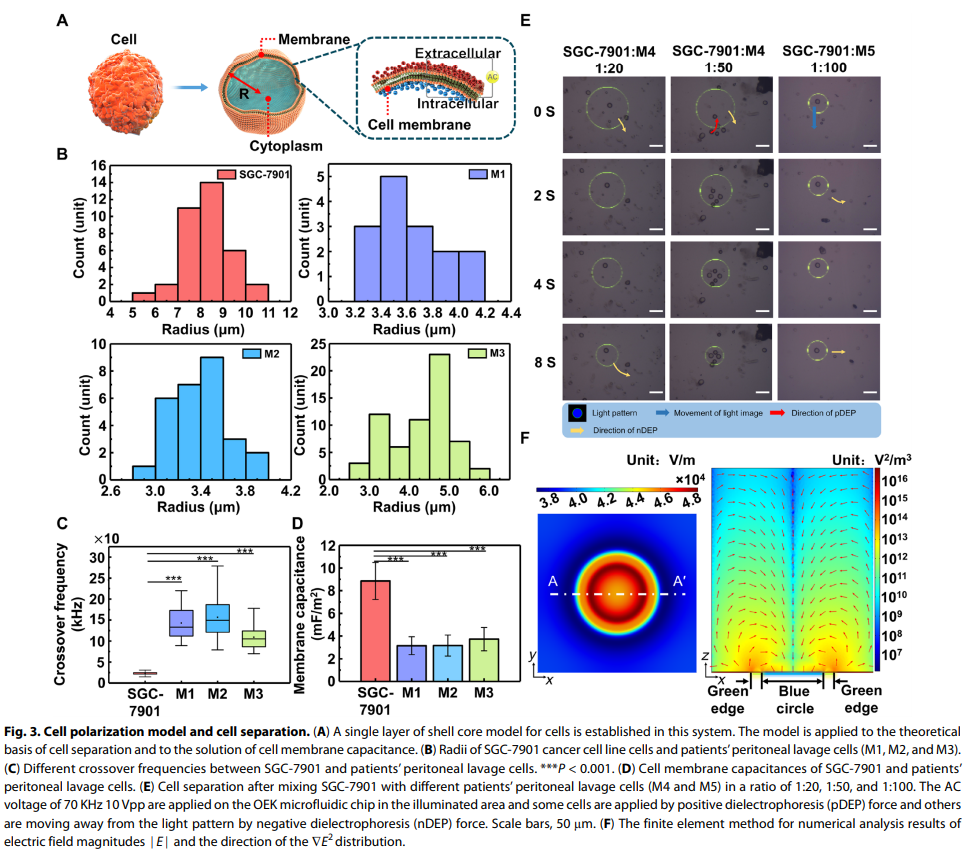
The researchers fabricated a novel OEK-based microfluidic chip to separate live gastric cancer cells from patients' ascites and characterize their electrical properties. They established polymerization model of cells and solution model of cell membrane capacitance.
The sizes and electrical characteristics between the gastric cancer cells and peritoneal lavage cells were significantly different. Thus the OEK method could theoretically separate gastric cancer cells from the ascites and peritoneal lavages.
Through experiments, the researchers separated gastric cancer cells from six patients' ascites with purity up to 71%. Compared with the traditional clinical peritoneal metastasis detection method, this new method solved the problem of low sensitivity.
It is also a label-free, non-destructive and rapid technique. The researchers could separate and collect gastric cancer cells in the OEK microfluidic chip in 5 minutes.
They also obtained the cell membrane capacitances of gastric cancer cells and peritoneal lavage cells. These digital data can be used as a bio-marker, as part of cellular information.


reference
"Detection and isolation of free cancer cells from ascites and peritoneal lavages using optically induced electrokinetics (OEK)" Science Advances (2020). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba9628
'medical engineering' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2D 물질을 이용한 도파민 센서 (0) | 2020.08.10 |
|---|---|
| personalized treatment를 위한 smart watch-drug concentration sensor (0) | 2020.08.10 |
| A new way to deliver drug by pressure. (0) | 2020.08.05 |
| hydrogel-solid bonding (0) | 2020.08.04 |
| drawn on skin sensor (0) | 2020.08.03 |


